A monopolist sells two products, X and Y . There are three consumers with asymmetric preferences. Each consumer buys either one unit of a product or does not buy the product at all. The per-unit maximum willingness to pay of the consumers is given in the table below.
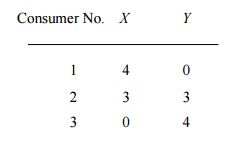
The monopolist who wants to maximize total payoffs has three alternative marketing strategies: (i) sell each commodity separately and so charge a uniform unit price for each commodity separately (simple monopoly pricing); (ii) offer the two commodities for sale only in a package comprising of one unit of each, and hence charge a price for the whole bundle (pure bundling strategy), and (iii) offer each commodity separately as well as a package of both, that is, offer unit price for each commodity as well as charge a bundle price (mixed bundling strategy). However, the monopolist cannot price discriminate between the consumers. Given the above data, find out the monopolist’s optimal strategy and the corresponding prices of the products.
Any idea how to solve this question? I have no idea how to calculate optimal pricing for a pure and a mixed bundle