Doubts!
|
1.Suppose annual growth rate of Nominal GDP, Real GDP and population are
respectively 8%, 4%, and 2%. Then the growth rate of real per capita GDP, and GDP deflator are respectively and . A. 4% and 2% B. 2 % and 4% C. 6% and 2% D. -2% and 4% Please explain the method! 2. If, marginal propensity to consume is 0.75, then the value of the balanced budget multiplier is A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 3. Which of the following will not result in an increase in output? A. An increase in autonomous spending B. A decrease in autonomous taxes C. An increase in autonomous taxes D. An increase in lumpsum taxes 4. A-(B U C)= a) A-B U A-C b)A-B INTERSECTION A-C 5. Let a 2 R. If x belongs to the neighbourhood Ve(a) for every e > 0, then: A. x > a B. x 6= a C. x < a D. x = a |
|
1. B
2. A 3. D 4. A 5. D ( explanation is pretty confusing , I don't rem myself , but yes , for this question , option D is the answer  ) )
"Once you eliminate the impossible, whatever remains, no matter how improbable, must be the truth."
|
|
For 1) GDP deflator=Nominal/Real, right? Won't we get 2 (8/4)? So shouldn't 2 and 2 be the answer?
For 3), won't increasing taxes reduce output? Also, aren't lumpsum taxes independent of output? |
|
In reply to this post by Bin
for 4 we can understand one thing that A-(BUC) it means a much portion is deducted....what is more 5-(2+3) or 5-(3-2), i think its the second one....A-(BUC)=(A-B) intersection (A-C).
|
|
In reply to this post by Bin
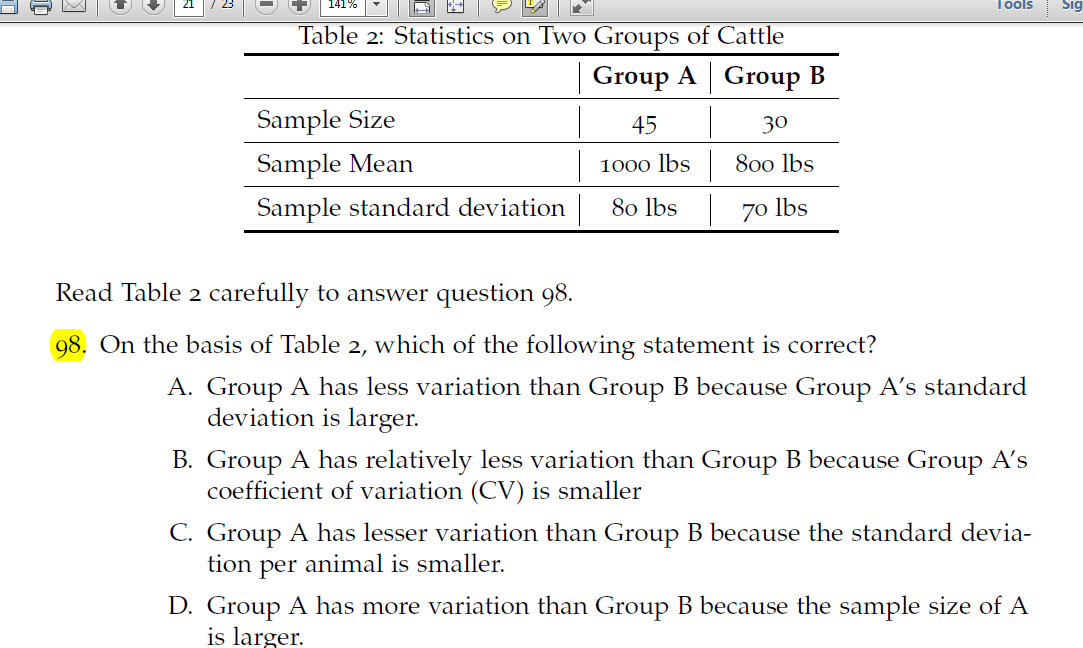 Please answer!! 2. A sample of 99 distances has a mean of 24 feet and a median of 24.5 feet. Unfortunately, it has just been discovered that an observation which was erroneously recorded as “30” actually had a value of “35”. If we make this correction to the data, then: A. The mean remains the same, but the median is increased. B. The mean and median remain the same. C. The median remains the same, but the mean is increased. D. The mean and median are both increased. 3. Relative Frequency of Accidents per day in a city Accidents 0 1 2 3 4 or more Relative Frequency 0.55 0.20 0.10 0.15 0 Which of the following statements are true on the basis of information provided in Table 1? 1. The mean and modal number of accidents are equal. 2. The mean and median number of accidents are equal. 3. The median and modal number of accidents are equal. A. 1 only. B. 2 only. C. 3 only. D. 1, 2, and 3. 4.The market structure of mobile telecom services in India is almost a: A. Perfectly competitive industry. B. Regulated monopoly. C. Bilateral monopoly. D. Oligopolistic industry. 5. 86. Which of the following items accounts for the largest share in total subsidies in India? A. Petroleum. B. Food. C. Fertilizer. D. Interest subsidy. 6.Which of the following statements with respect to aggregate savings and investment in India is true: A. Aggregate savings rate is less than aggregate investment rate. B. Aggregate savings rate is more than aggregate investment rate. C. Aggregate savings rate is equal to aggregate investment rate. D. Aggregate savings rate has been falling continuously since 1991 with increases in consumption. 7. Much of India’s GDP growth is contributed by: A. Primary and secondary sectors. B. Information and communications sector. C. Manufacturing and mining sectors. D. Tertiary sector including construction. 8. When there is an absence of money illusion, the consumer’s demand function is said to be homogeneous of degree . A. Zero. B. One. C. Two. D. More than 2. 9. If the rows in a matrix A are linearly independent, the matrix A is . A. singular. B. Non-singular. C. Symmetric. D. Idempotent. 10. If you are measuring level of consumption of a good in one axis and that of a bad on the other axis, the indifference curve will be: A. Parallel to the good axis. B. Parallel to the bad axis. C. Of “inverted-U” shape. D. Having positive slope. 11. In a perfectly competitive market, a firm’s long-run supply curve is: A. The upward segment of its average cost curve. B. The upward segment of its marginal cost curve. C. The upward segment of its marginal cost curve which is above the lowest point of the average cost curve. D. None of the above. 12. Theory of revealed preference is used to: A. Derive optimal choice from given preferences and budget constraint. B. Derive underlying preferences from optimally chosen bundles under different budget constraints. C. Both A and B. D. Neither A nor B. 13. Marginal utility of an inferior good is: A. Positive. B. Negative. C. Zero. D. Zero or positive. 14. Consider a paddy farmer’s production decision, which of the following input does not enter into his optimisation programme? A. Labour. B. Fertiliser. C. Sunlight. D. None of the above. 15. If the nominal interest rate is 8%, prices are rising at 5% a year and GDP is growing at 6% a year, then the real interest rate in the economy is: A. 2% B. 5% C. 3% D. -3% 16.If real GDP, population and prices are increasing respectively at 8%, 2.5% and 5% per annum, then growth rate of real per capita GDP is: A. 10.5% B. 8% C. 5.5% D. 6% PLEASE REPLY!!! |
«
Return to General Discussions
|
1 view|%1 views
| Free forum by Nabble | Edit this page |

