Points of discontinuity (holes and vertical asymtotes)
123



123
|
Hello sir,
When a question is asked to identify points of discontinuities, should we be looking for 'infinite' (vertical asymptotes) discontinuities also? 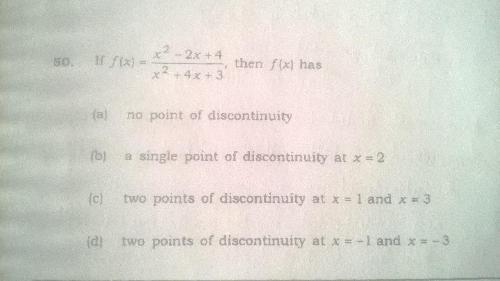 For the above example should we choose option a) or d)? |
|
D because points of discontinuity exists even after term cancellation whereas asymptote disappears if terms cancel out
|
|
This post was updated on .
Here we have only vertical asymtotes, no term is getting cancelled. I wanted to know if we consider those points which are not in the domain of the function. Thank you.
|
|
X and Y are independent random variable. Let Vx and Vy denote the variance X and Y, respectively. let the random variable Z be defined to be [aX+ bY], where a and b are 2 positive real numbers. It is known that (i) Vy is strictly larger than 1, (ii) variance of z is 1 and (iii) covariance between Y and Z is 1. In term of Vx and Vy what are a and b?
|
|
Not sure, if this is right, but I got a=square root((1/Vx)-(1/VxVy)), b= 1/Vy.
|
|
This post was updated on .
getting the same ans. but again not sure if it's the right way to proceed
One more query, Qd= 100 - 2P Qs= 3Ps and tax imposed is rs 1 per unit of output. post tax equilibrium, Producers price and consumer's price? I'm getting post tax Q = 58.8 suppliers receive = 19.6 consumers pay = 20.6 please confirm? |
Re: Points of discontinuity (holes and vertical asymtotes)
|
In reply to this post by Vidhya
Vidhya I've got the same answer as well
|
|
In reply to this post by soimmoi
I too got similar values for ps and pd.
|
Re: Points of discontinuity (holes and vertical asymtotes)
|
same here!
|
|
In reply to this post by Vidhya
Can you please confirm if this is the right way to solve this:
For an economy , the long run rate of growth of GDP is 5% at full employment . The inv. rate is 20% and the rate of growth of labour force is 2%.then the capital output ratio is a:2 b:5 c:7 d:10 The answer is 10. Should we use natural rate of growth here (which is equal to growth rate of labour 2%) and then using gn = s/theta (2% = 20%/theta)to get theta = 10. |
|
Yes, 10 is the ans. I've done it in the same way, it's a lil weird question.
can you see these two as well suppose critical region for a test statistics S in a given test of significance is given by S1<= S <=S2. Suppose the P( S<S1) = 0.3 and P(S> s2) = 0.45. what is the level of significance used in carrying out this test? a) 0.03 b)0.48 c) 0.52 d)0.42 my sol: c consider a society of 2 individuals in which a single commodity is produced, individual 1 getting x units of commodity and individual 2 getting y units of commodity. suppose only 3 outcomes are possible in any time period A : X=10, Y=10 B: X=7, Y=5 C: X=5, Y=12 a) society prefer B over C b) Society prefer C over B C) soiety will be indifferent b/w b and c d) We cannot say which of (a) (b) (c) will hold An individual ranks bundles (x,y) and (x*, y*) in following manner: if either x> x* or x= x* and y>y*. if individual prefer x,y to x*,y*. given that individual income is 100 and px= 2, py= 1, individual will purchase every week a) 25 units of x and 50 units of y b)100 units of y c)50 units of x d) 45 units of x and 10 of y |
|
1-(0.45 +0.3) = .52
Considering a fair distribution, I think A would be preferred to B which would be preferred to C. A : X=10, Y=10 B: X=7, Y=5 C: X=5, Y=12 so a) society prefer B over C. Not sure though. For lexicographic preferences x= 100/px = 50 units of x |
|
I think so for 2nd one we can't say which of a b c holds because fair allocation is not always pareto optimal AND for 3rd how can you say x is lexographic to y?
|
|
In reply to this post by Vidhya
A monopolist manufactures widgets. The quantity, q that the monopolist produces must be a non-negative integer. The total cost C(q) of producing q units is C(q) = 10q. The inverse demand curve for widgets is p(q) = 20/q, where p denotes the market price of widgets. What is the monopolist’s profit maximizing q?
(a) The problem does ot have a solution. (b) 1 (c) Infinity (d) 0 Solving using MR=MC does not give any solution, but q=1 gives the maximum profit (for q >0). Is this approach correct? |
|
In reply to this post by Vidhya
A is the ans for your ques
one more query a group of persons has mean age 12, and median 10. P( randomly selected person will be 12 years or older is) a) 0.5 b) less than 0.5 c) <= 0.5 d) greater thhan 0.5 i think so b |
|
Thank you.
P(X>10)= P(X<10) = .5, c should be correct <=5 consider : 8 8 8 12 16 20, mean = 12, median = 10, here P(X>=12) = 0.5 |
|
thank you so much.
|
|
This post was updated on .
In reply to this post by Vidhya
An individual who spends his entire income purchasing 2 goods is seen to purchase the following bundles of 2 goods in three situations:
Bundle A : (100,10) When prices of good are (1,10) Bundle B : (50,15) " " " " " (5,1) " C: (40,20) " " " " " (4,4) Is is possible to infer prefrence over bundle A,B,C?? i think so yes A preferred to both B & C. can't say anything about b&c preference order. Q2) Given: Depreciation allowances 200 Personal (direct) tax payments 250 indirect business taxes 200 corporate (profits) taxes 100 Dividend Payments 50 undistributed profits 50 Government transfer payments 200 personal consumption expenditure 1200 personal savings 100 Calculate: 1) personal income 2) Net national product 3) national income 4) Gross national product |
Re: Points of discontinuity (holes and vertical asymtotes)
|
In reply to this post by Vidhya
Hey Vidhya, the demand curve here is a hyperbola and the area underneath in the form of total revenue would be a constant for all combinations of price and quantity. Therefore cost is minimised at q=1 like you said
|
|
In reply to this post by soimmoi
1. should be A preferred over B preferred over C
2. not totally sure, my best guess PI=1050 NNP=1200 NI=1000 GNP=1400 let me know what your answers are. also, in which year did they ask this? i don't think they ask this kind of questions anymore |
«
Return to General Discussions
|
1 view|%1 views
| Free forum by Nabble | Edit this page |

