Hi Sonia..it
Do you have the answer key..i think the answer should be b
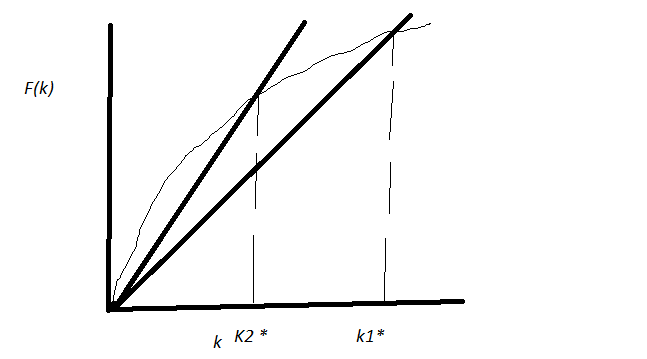
a) cause a reduction in rate of growth in output per worker in long run- reduction in savings will reduce the steady state value of output per worker.But at the new steady state,as in the old one,growth of output per worker in the long run will be zero-hence a is wrong
b) have a negative effect on rate of growth in output per worker in short run- the reduction will mean that new the new steady state will be at a lower k. Initially the economy was at steady state ,hence delta K/=population growth rate+depreciation. Again to settle at a lower steady state, growth rate of k must be negative. let f=AK^a*N^b & a+b=1.Then output per worker y=Ak.Therefore rate of growth of output per worker will be proportional to rate of growth of k.Hence,it will be negative.
C) hve no effect on level OF output per worker in long run- The new steady state capital per worker is obviously less than the the previous one.Hence output per worker will be less.Hence c is incorrect
d) cause an increase in level of output per worker in long run- incorrect from the previous argument
I am not 100% sure.It is just an attempt.
Thanks